High-level workflow
- In KnowledgeAI™:
- Add the external knowledge base.
- Test the CMS integration using the Answer Tester tool.
- Expose the articles to agents by integrating KnowledgeAI into your Conversation Assist solution, or expose them to consumers by integrating KnowledgeAI into a LivePerson Conversation Builder bot.
Add an external KB without LivePerson AI
- Click Add Knowledge Base in the upper-right corner.
-
In the window that appears, select the Other Connection tab, and then select External Knowledge Base without LivePerson AI.
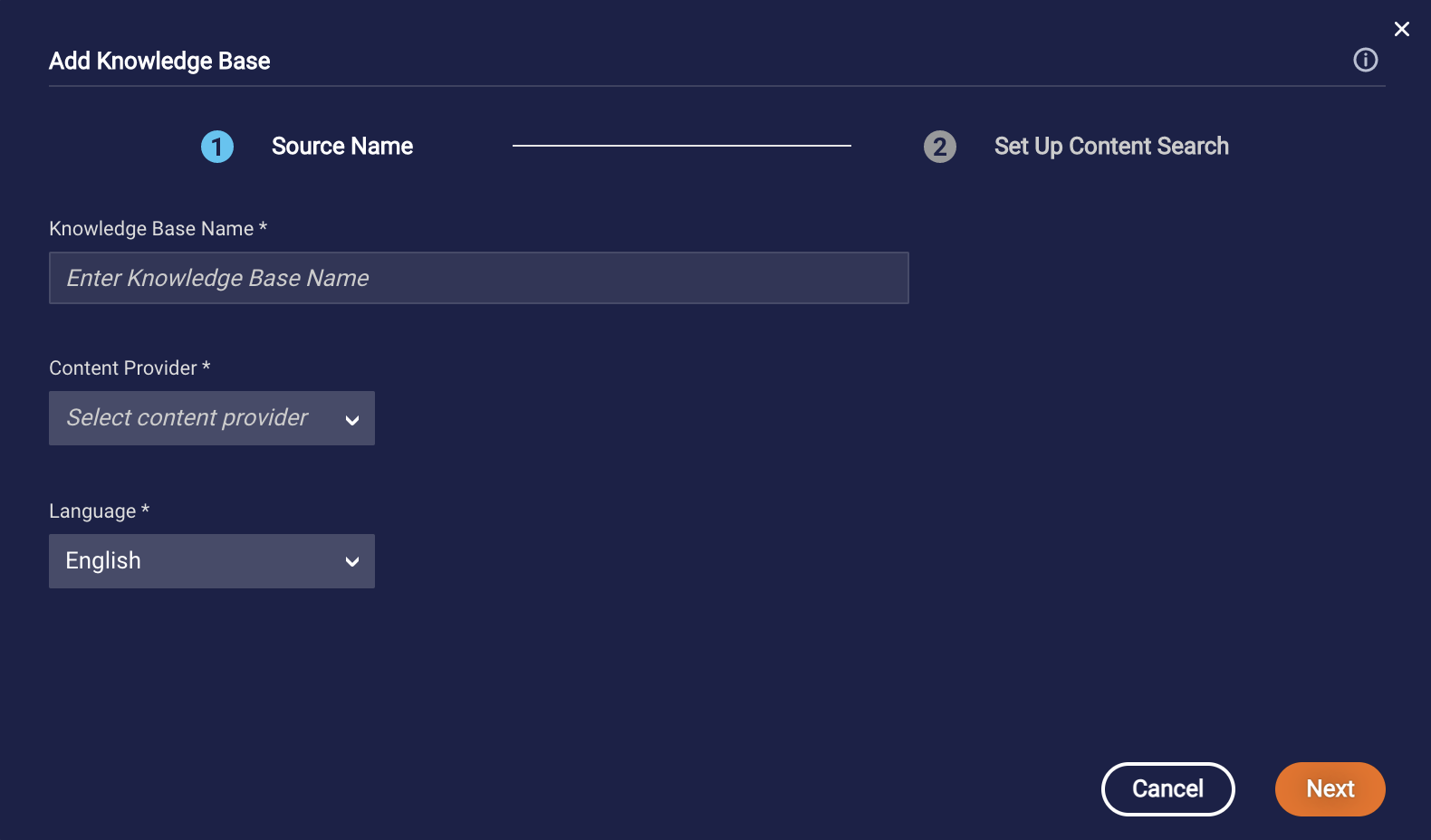
- Specify the following:
- Knowledge Base Name: Enter a descriptive name, e.g., “Technical Support FAQs.”
- Content Provider: Select the name of the content provider. If the provider isn't listed, select "Other," and enter the name.
- Language: Select the language of the content. This setting is informational only and doesn't affect the behavior of the knowledge base.
-
Click Next.
-
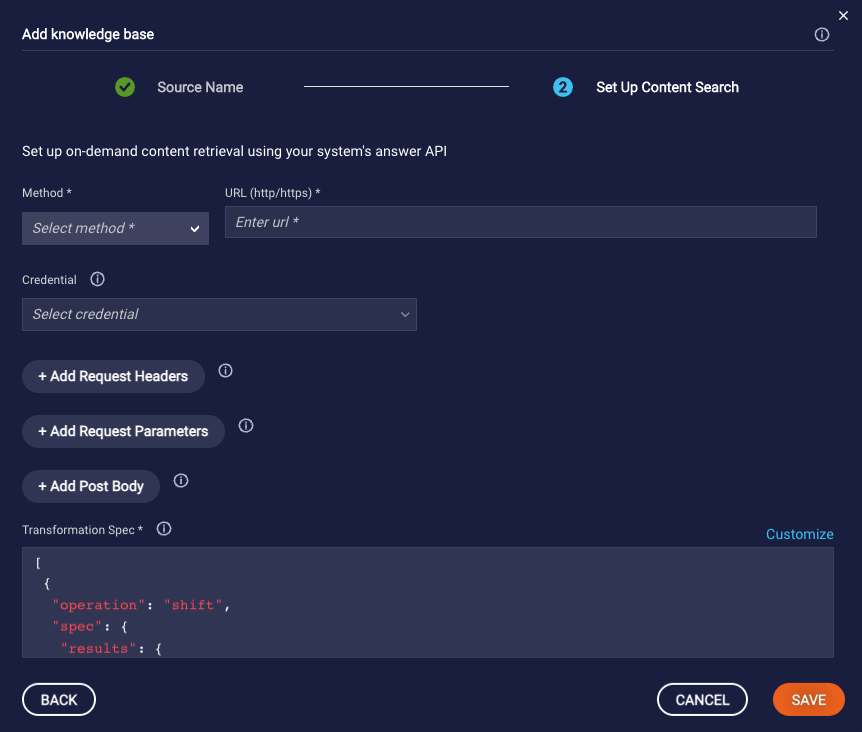
Define the request for the on-demand content retrieval using your CMS' query and answer API. To pass the input phrase to use when performing the search in the CMS, you must use the {inputPhrase} placeholder that's provided as per your CMS' API contract: in the URL, in the request parameters, or in the post body.
The request should return the best article matches. Each article must contain a title and at least one of these content attributes: summary, detail, contentURL, imageURL, videoURL, or audioURL.
- Method: Select the type of HTTP request method.
- URL: Enter the request target, the URL.
- Credential: Select the credential to use for authorization if applicable.
- + Add Request Headers: Add any request headers to include in the request.
- + Add Request Parameters: Add any request parameters to pass in the URL’s query string.
- + Add Post Body: Enter the payload to send if applicable.
-
Transformation Spec: If you were able to select your Content Provider in Step 3 above, a default spec is provided here. You can use it if you haven't customized the CMS' data model. If you weren't able to select your content provider, a default spec isn't provided.
Here, provide a Jolt transformation spec that can be used to "transform" the response into the LivePerson KnowledgeAI article schema. In other words, given the request, map the article suggestions/answers data model (schema) to the LivePerson KnowledgeAI data model.
- Click Save.
Test the CMS integration
After you've add an external knowledge base that doesn't use AI, you can test the integration with the Search tool. This involves entering a consumer utterance to see and evaluate the results that are retrieved from the CMS.
To test the CMS integration
- Open the knowledge base.
-
Click Articles in the menu in the upper-left corner.
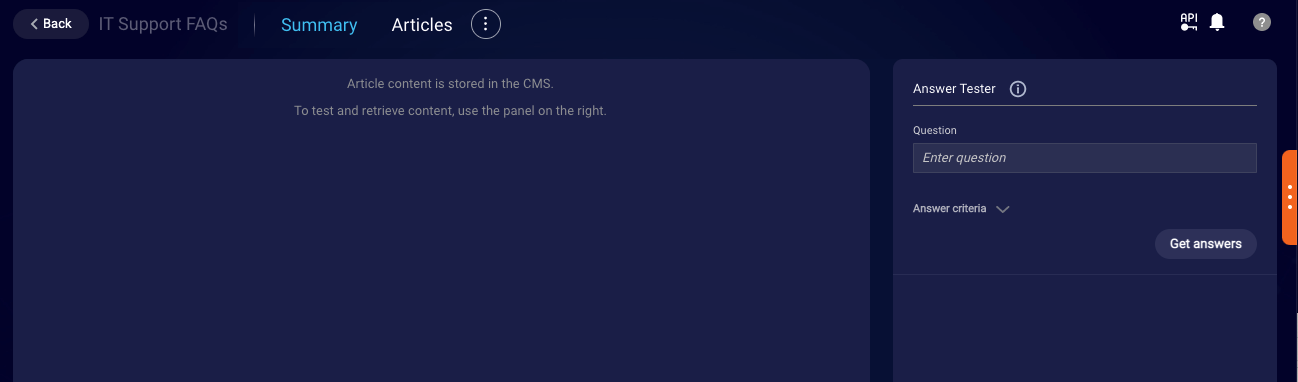
Initially, the Articles page doesn’t show any metadata or content because, with this type of external knowledge base (one without LivePerson AI), only configuration information is stored within KnowledgeAI. The content remains in the CMS.
-
Enter an utterance in the Answer Tester on the right, and click Get answers.
This performs a search against the CMS.
-
Evaluate the article results that are displayed. If they aren't what you expect, you might need to adjust the knowledge base's configuration.
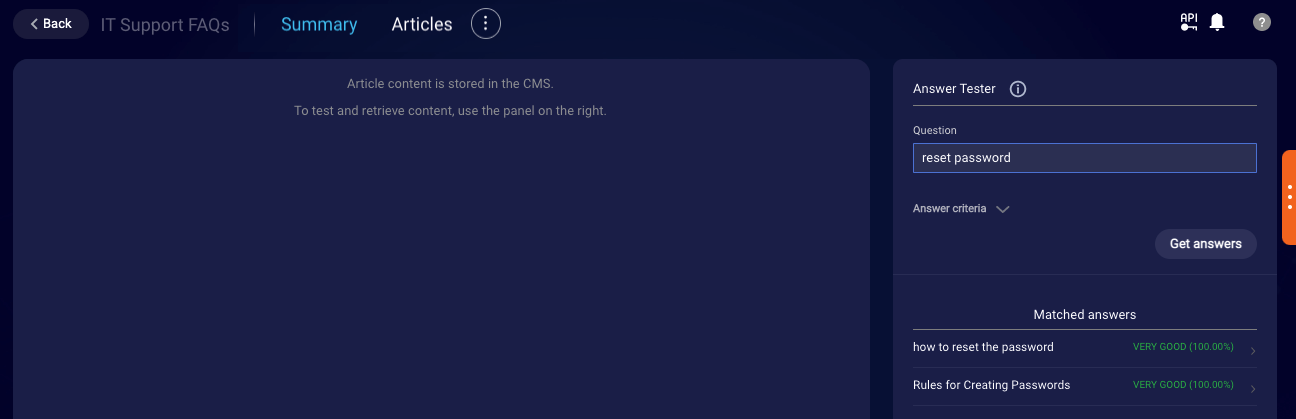
Answers are evaluated by your external CMS. When they're returned, they're always assumed to be a match.