This section will describe the responses that are expected to be sent by the Send Conversation Events endpoint of the Custom Endpoint service. To ensure the validity of the response, brands can use our Conversation Tester feature. In the case of Structured Content validation, you can also leverage this tool.
Sending Encoded Metadata
The Conversational Cloud Messaging platform provides a new metadata input type (“encodedMetadata”) for passing a base64 encoded metadata on a conversation. The new metadata input type is in addition to the existing conversation metadata input field. Third-party Bot also supports this property and this section will cover the information needed for you to send encoded metadata within your conversations. Before sending encoded metadata you must ensure the following conditions in order to successfully send the data.
- Common.EncodedMetadata AC feature is ON
- Content is base64 encoded
- Metadata size is limited to 5k
Failing to comply with the above validation points will cause the message to be dropped. This feature is only available for messaging conversations, not for chat conversations
Sending Text Message with Encoded Metadata
You can send encodedMetadata with a simple text message an example of such a response can be seen in Figure 4.1. More information on responses expected by Third-Party Bot Connector can be found at API Service Specification
{
"response": [
{
"type": "TEXT",
"data": {
"message": "This is a text with encoded metadata",
"encodedMetadata": "ewoic29tZUluZm8iOiAiSSB3YXMgZW5jb2RlZCIKfQ==",
"metadata": [{ "type": "ExternalId", "id": "ABCD1234" }]
}
}
],
"analytics": {
"intents": [
{
"id": "base-encoded-metadata-text",
"description": "Encoded Metadata Text Messages",
"confidenceScore": 1
},
{
"id": "base-text",
"description": "Text Messages",
"confidenceScore": 0.99
}
]
}
}
Figure 4.1 Showing example response of a text with encoded metadata
Sending Rich Content (structured content) with Encoded Metadata
You can send encodedMetadata with a structured content message an example of such a response can be seen in Figure 4.2. More information on responses expected by Third-Party Bot Connector can be found at API Service Specification
{
"response": [
{
"type": "STRUCTURED_CONTENT",
"data": {
"metadata": [{ "type": "ExternalId", "id": "ABCD1234" }],
"encodedMetadata": "ewoic29tZUluZm8iOiAiSSB3YXMgZW5jb2RlZCIKfQ==",
"structuredContent": {
"type": "vertical",
"elements": [
{
"type": "button",
"click": {
"actions": [
{ "text": "Recommend Me a movie!", "type": "publishText" }
]
},
"title": "Recommend Me a movie!"
}
]
}
}
}
],
"analytics": {
"intents": [
{
"id": "base-encoded-metadata-sc",
"description": "Encoded Metadata SC Messages",
"confidenceScore": 1
},
{
"id": "base-sc",
"description": "SC Messages",
"confidenceScore": 0.99
}
]
}
}
Figure 4.2 Showing an example response of structured content with encoded metadata
Sending Pause/Delay Message
It is possible to send an event of type "delay" before regular content events and actions. This specifies the time the bot will wait before displaying the next message. An example of such a response can be seen in Figure 4.3 where one text message is displayed then 5 seconds of delay and after that, a structured content is presented. More information on responses expected by Third-Party Bot Connector can be found at API Service Specification
{
"response": [
{
"type": "TEXT",
"data": {
"message": "Please wait while I prepare to give you options!"
}
},
{
"type": "DELAY",
"data": {
"seconds": 4,
"typing": true
}
},
{
"type": "STRUCTURED_CONTENT",
"data": {
"metadata": [
{
"type": "ExternalId",
"id": "ABCD1234"
}
],
"structuredContent": {
"type": "vertical",
"elements": [
{
"type": "button",
"click": {
"actions": [
{
"text": "Recommend me a movie",
"type": "publishText"
}
]
},
"title": "Recommend a movie"
}
]
}
}
}
],
"analytics": {
"intents": [
{
"id": "base-delay",
"description": "Delay Message",
"confidenceScore": 1
},
{
"id": "base-all",
"description": "Mix Messages",
"confidenceScore": 0.99
}
]
}
}
Figure 4.3 Showing an example response of structured content with encoded metadata
Sending Private Text Message
It is possible to send a private text message from the Live Engage (LE-UI) via the agent workspace. This feature can now be used via Third-Party bots as well. This will allow brands to define private message text within the conversational flow of the bot. These messages are published in the conversation for other Agent/Manger participants. This enables Brands to customize messages giving more insight, summarizing actions taken by the bot, or also advising on the next actions the handover agent should take. Please note private text messages will never be shown to the consumer and will be visible only inside the conversation window of the agent workspace.
Please note If you have not migrated to the new Agent Workspace you will not be able
to see the Private message indicator in the conversation window. Nevertheless,
private text messages will not be shown to the consumer and only remain visible
to Agents and Managers.
An example of such a response can be seen in Figure 4.4. More information on responses expected by Third-Party Bot connector can be found at API Service Specification
{
"response": [
{
"type": "TEXT",
"data": {
"message": "I am hidden from the customer",
"messageAudience": "AGENTS_AND_MANAGERS"
}
},
{
"type": "TEXT",
"data": {
"message": "This is a normal text"
}
}
],
"analytics": {
"intents": [
{
"id": "base-all",
"description": "Mix Messages",
"confidenceScore": 1
}
]
}
}
Figure 4.4 Showing an example response of private text and a normal text
Invoke LivePerson Function
During a conversation, it is possible to trigger a LivePerson Function that is deployed to the LivePerson Functions (Function as a Service) platform. We provide a way to run custom logic with a bot. You need to ensure that the LivePerson Function is deployed and running. Furthermore, the user can provide a payload as well that will be sent to the LivePerson function while invocation. The invoke response is considered an action response. An example of such a response can be seen in Figure 4.5.
Please note we only support ONE ACTION per response
{
"response": [
{
"type": "TEXT",
"data": { "message": "I will invoke a function after this text" }
},
{
"type": "ACTION",
"data": {
"name": "INVOKE_FUNCTION",
"parameters": {
"lambdaUuid": "4f9c233a-e7e6-4af3-b680-59ba20ab8962",
"payload": { "message": "I am invocation function payload" }
}
}
}
],
"analytics": {
"intents": [
{
"id": "base-invoke",
"description": "Generic invocation Intent",
"confidenceScore": 0.95
}
]
}
}
Figure 4.5 Showing an example response of invoke LivePerson function
The bot does not escalate on a failed invocation by default. To enable this, set the additional
parameter failOnError to true. An example of such a response can be seen in Figure 4.6
{
"response": [
{
"type": "TEXT",
"data": {
"message": "I will invoke a function after this text that cause escalation on failure"
}
},
{
"type": "ACTION",
"data": {
"name": "INVOKE_FUNCTION",
"parameters": {
"lambdaUuid": "4f9c233a-e7e6-4af3-b680-59ba20ab8962",
"payload": { "message": "I am invocation function payload" },
"failOnError": true
}
}
}
],
"analytics": {
"intents": [
{
"id": "base-invoke",
"description": "Generic invocation Intent",
"confidenceScore": 0.95
}
]
}
}
Figure 4.6 Showing an example response of invoke LivePerson function with failOnError property
Sending SIGNALED events (Messaging Only)
This Feature requires UMS 4.9
To send a signal to the channel not visible inside the normal conversation a bot can send the following event. Channels need to implement custom logic and listen on chat state events in order to react to it.
{
"response": [
{
"type": "ACTION",
"data": {
"name": "SIGNAL",
"parameters": {
"payload": {
"test": "value"
}
}
}
}
],
"analytics": {
"intents": [
{
"id": "signal-request",
"description": "customer side requested a signal",
"confidenceScore": 1
}
]
}
}
Engagement attributes (SDES) as context
Third-Party bots allow the collection of engagement attributes (more information can be found
here) if Engagement Attributes
option is checked in the Conversation Type step as shown in Figure 2.4.
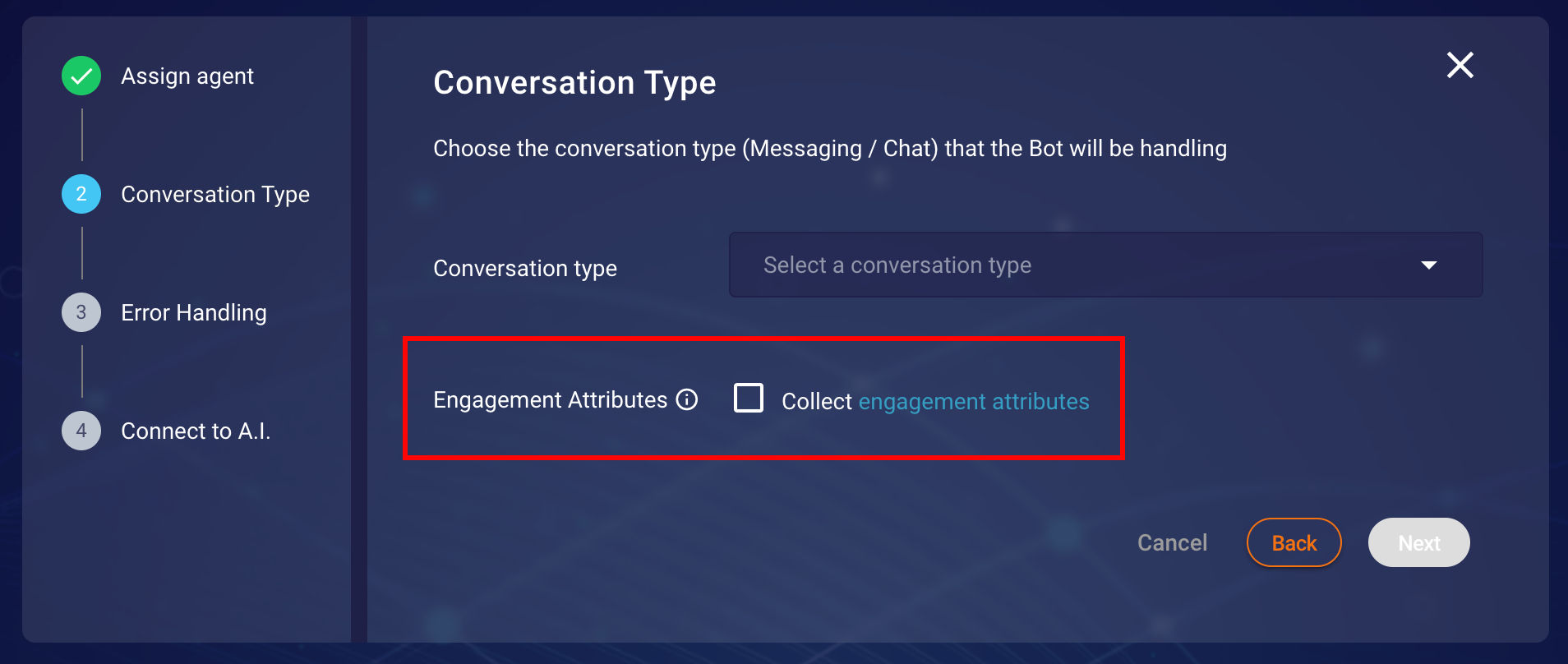 Figure 2.4
Figure 2.4 Conversation Type step in creation/modification of bot configuration.
These attributes are only collected at the start of a conversation. we send those engagement attributes when the Third-Party Bot connector calls the Create Conversation endpoint of the Custom Endpoint service.
Third-Party bots leverage the LivePerson Visit Information API to collect the engagement attributes, Further information on Visit Information API can be found here. Moreover, Engagement attributes are not updated throughout the life cycle of a conversation and are only passed along with each message request.
Receiving Rich Content Response (Messaging Only)
Third-Party Bots allow LivePerson's Rich Messaging channel capabilities not only to be received as a response from the vendor but also, to allow Rich Messages(Structured Content) to be sent back to the vendor based on specific user interactions/responses (For example user sharing their location on WhatsApp). Please note these capabilities are sometimes limited by the channels in which the conversation is happening. For the list of Rich Messaging capabilities for each channel, browse or search the table here.
An example of a request body of Rich Content Event (of type map) sent by Third-Party Bot
container to Custom Endpoint service can be seen in Figure 4.7. More information on the request
expected by Third-Party Bot Connector can be found at API Service Specification.
{
"type": "RICH_CONTENT",
"source": "CONSUMER",
"data": {
"content": {
"type": "vertical",
"elements": [
{
"type": "map",
"la": 49.43180847167969,
"lo": 7.755561351776123,
"alt": "49.43180847167969, 7.755561351776123"
}
]
}
},
"context": {
// here comes context information
}
}
Figure 4.7 An example of Rich Content Event request sent by Third-Party Bot connector to Custom Endpoint service
Some important things to notice here are
- The request body contains
typewhich identifies that the content type isRICH_CONTENT - The actual body of the Rich Content Event can be accessed via
data.contentproperty
A demo of our WhatsApp map example with the response from an example custom endpoint service can be seen in Figure 4.8:

Figure 4.8 A Demo of sending raw response back from Custom Endpoint Service on receiving Rich Content Event
Receiving Last consumer message (Messaging Only)
When an ongoing conversation gets transferred to a bot connected via the Third-Party Bot connector, the connector forwards the last consumer message to the AI vendor as part of the the welcome event. This allows the bot to react to the last consumer message instead of instantiating a new conversation.
In the Custom Endpoint service, the last consumer message is passed via the property lastConsumerMessage that is sent with context information as part of lpEvent data. An example of the request body containing the WelcomeEvent is provided below:
{
"type": "START",
"source": "CONVERSATION",
"data": {},
"context": {
"lpEvent": {
"type": "ContentEvent",
"contentType": "welcome",
"lastConsumerMessage": "I need to return my order"
}
}
}
Send Secure Forms (PCI)
Secure forms are configured by LivePerson. To enable this feature, please contact LivePerson customer support or your account team. Your LivePerson account team will work with you make the necessary adjustments to your account settings and configurations. For additional information regarding secure forms: Community Center
To give agents the permission to read secure forms sent by a bot, please contact LivePerson customer support to enable the site setting: messaging.display.secure.form.sent.by.bots
Bots are able to send a secure form to a conversation and transfer the customer after submission. The transferred conversation is then visible by an eligible agent, that can read and process the submitted form data.
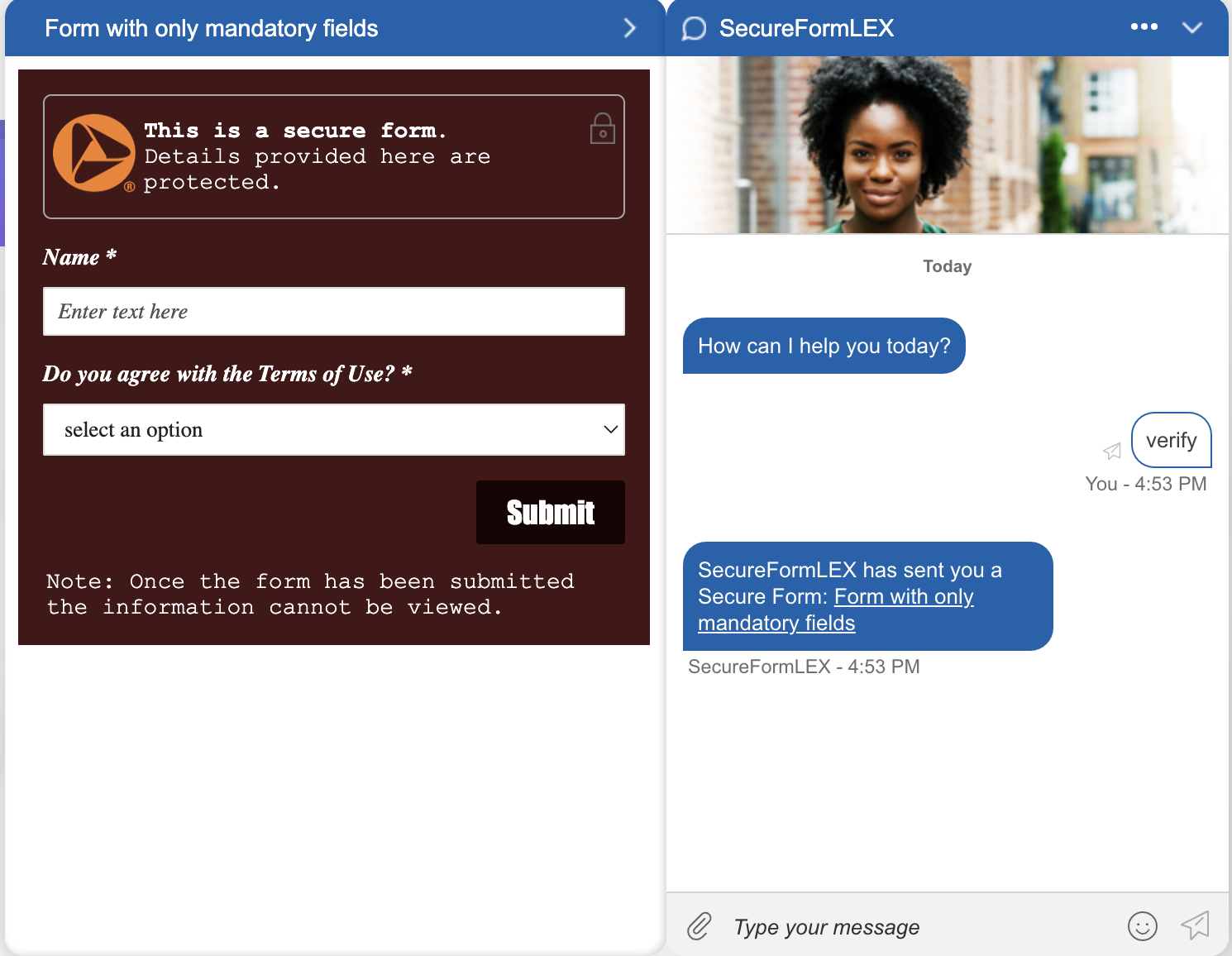
To enable this feature for Custom Endpoint, you need to create a new Intent with a matching utterance and a customisable payload response to it. The payload needs to send a SEND_SECURE_FORM action including the unique formId of the form,that should be provided from LivePerson after the creation of one secure form, and the title of the form.
{
"type": "ACTION",
"params": {
"action": "SEND_SECURE_FORM",
"data": {
"formId": 4510014332,
"title": "Form with only mandatory fields"
}
}
}
{
"response": [
{
"type": "ACTION",
"data": {
"name": "SEND_SECURE_FORM",
"parameters": {
"formId": 4510014332,
"title": "Form with only mandatory fields"
}
}
}
],
"analytics": {
"intents": [
{
"id": "secure-form",
"description": "Secure Form",
"confidenceScore": 1
}
]
}
}
To transfer the conversation after submission to an eligible user that can process the secure forms, you need to create a new intent listening on the utterance FORM-SUBMISSION-INTENT that transfers the conversation using a basic transfer event.
Enable mTLS for Custom Endpoint
The Custom Endpoint Vendor supports additional mTLS-based authentication via LivePerson's internal mTLS forwarding service.
Note: mTLS permissions are configured by LivePerson. To enable this feature, please contact LivePerson customer support or your account team. Your LivePerson account team will work with you to make the necessary adjustments to your account settings and configurations, especially enabling the AC features: Common.lp-mtls-ui.MTLS.Self_Service and Common.MTLS_enabled. For additional information regarding MTLS, refer to the Community Center.
Third-Party Bots uses an App Installation for authentication with the mTLS service. Find the installation guide here. Please contact the LivePerson account representative (other contact options: chat with us on this page, or message Support) to ensure you have already installed the app. The example payload for App Installation can be found below (Note the scope value, which must be mtls.external).
{
"client_name": "mTLS Ce bot",
"description": "Custom Endpoint bot that uses MTLS",
"scope": "mtls.external",
"grant_types": ["client_credentials"]
}
mTLS Self Service
After enabling the account to use mTLS, a certificate must be created or requested and then uploaded in the mTLS Self-Service Application mTLS Self Service. This certificate must be assigned to a Service and then mapped to every available endpoint using the Custom Endpoint bot's configured base domain. The following endpoints must be mapped to the certificate within the mTLS Self-Service:
https://your-base-domain.com/api/v1/bots/*/environments
https://your-base-domain.com/api/v1/bots/*/environments/*/state
https://your-base-domain.com/api/v1/bots/*/environments/*/conversations/*
https://your-base-domain.com/api/v1/bots/*/environments/*/conversations/*/events
Bot Alignments
When creating or editing a bot in the Third-Party Bots Wizard and configuring the Custom Endpoint Vendor, you must first select an authentication service for the Custom Endpoint Service itself. This can be either an OAuth2 service or an App Installation with the thirdpartybots.customendpoint.bot scope.
Note: The selected OAuth2 service or App Installation will provide the authentication token that is sent in the Authorization header to the Custom Endpoint Service.
New mTLS Configuration:
- Enable mTLS: Enable the Enable MTLS switch. This activates the dedicated mTLS configuration.
-
Select mTLS App Installation: Choose the App Installation specifically for mTLS, which has the
mtls.externalscope, as shown in Figure 4.9.1.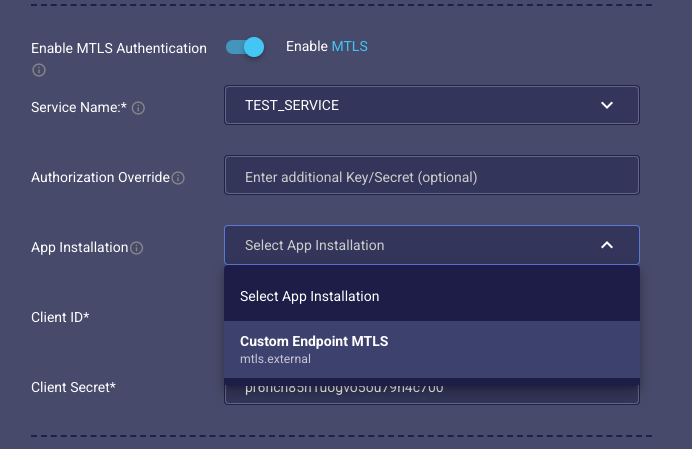
Figure 4.9.1: Third-Party Bots mTLS App Install Selection.
-
Select Service: Select the same Service that the certificate was assigned to in the mTLS Self-Service Application (Figure 4.9.2).
-
Authorization Overwrite (Optional): Below, you'll find the Authorization Overwrite field. This field is optional. By default, it sends the Bearer token from the initially selected authentication service (OAuth2 or
thirdpartybots.customendpoint.botApp Installation):{ "Authorization": "Bearer a2df5a65269165082b22e36278473c7009845b40b305b90248f15a3994f6f055" }You can override this by entering a secret or app key in the field.
Important: Test connections also use mTLS. Ensure your custom endpoint service and the mTLS configuration are aligned with this new flow, or the tests will fail.
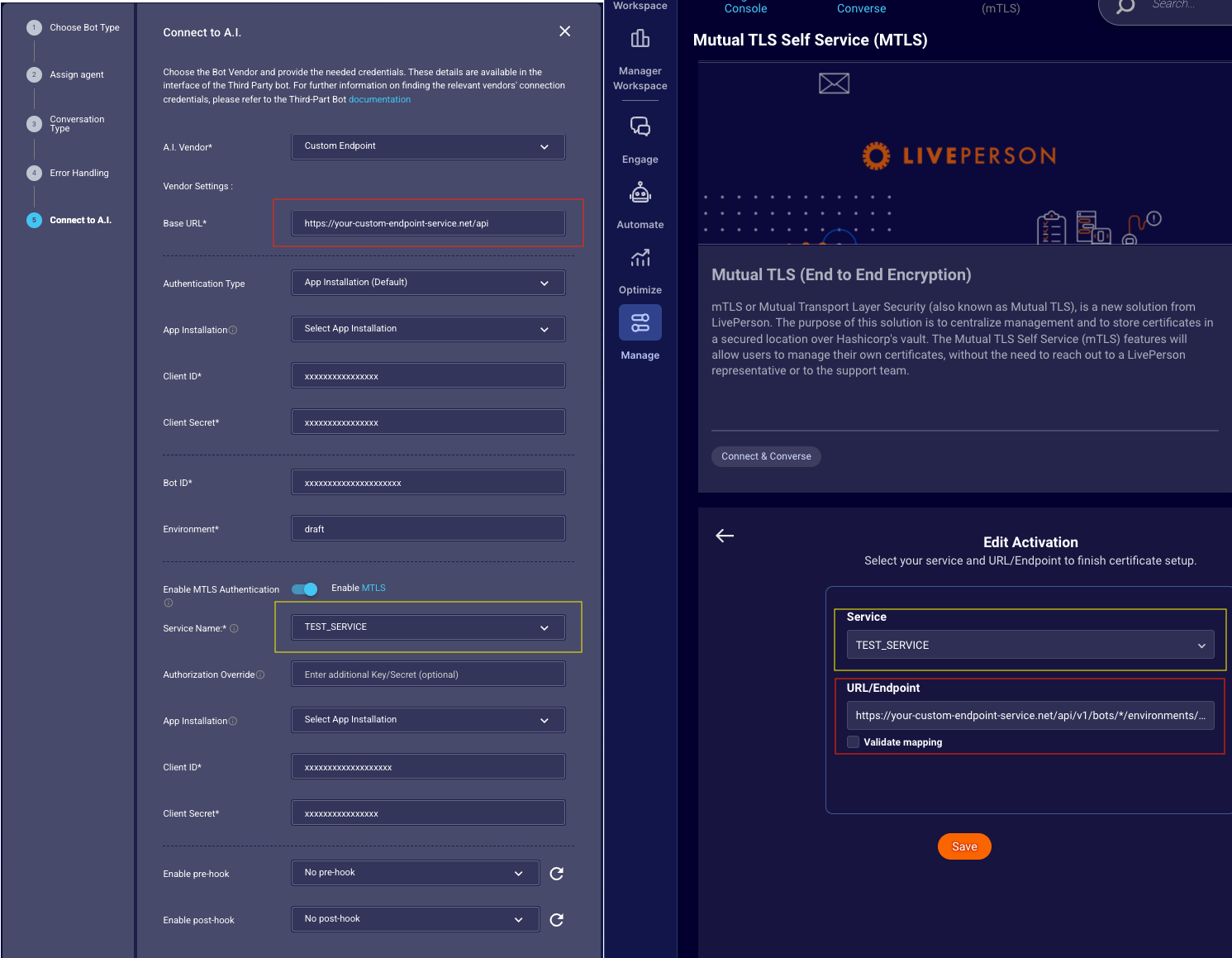
Figure 4.9.2: Side to Side View - MTLS Self Service and Third-Party Bots
Necessary Service Alignments:
-
Certificate Presentation: The Custom Endpoint Service server must present its matching certificate to perform the mTLS handshake. The certificate validation in the mTLS Self-Service can be used to test this.
-
Authorization Token Validation (Optional): While optional, validating the authorization token provides additional security. If you choose to validate it, ensure your service is aligned with the authentication method you are using:
- If using App Installations, the service must be aligned to use Sentinel V2 instead of Sentinel V1.
- If using OAuth2, the service must be aligned to verify the OAuth2 token.
Receiving signaled events (Messaging Only)
This Feature requires UMS 4.9
If SIGNALED events are enabled in the Conversation Type settings the bot will be able to receive this kind of chat state events.
{
"type": "SIGNAL",
"source": "CONSUMER",
"data": {
"content": "" // the metadata payload string
},
"context": {
// here comes context information
}
}