As the LivePerson functions feature uses LivePerson Functions, it's required to enable FaaS Admin permissions. To be able to implement your own LivePerson Functions, you will also need to enable FaaS Developer permissions. Take a look at this Getting Started Guide for more information on setting uo LivePerson Functions and its permissions.
Sending Encoded Metadata
Conversational Cloud Messaging platform provides a new metadata input type (“encodedMetadata”) for passing a base64 encoded metadata on a conversation. The new metadata input type is in addition to the existing conversation metadata input field. Third-party Bot also supports this property and this section will cover the information needed for you to send encoded metadata within your conversations. Before sending encoded metadata you must ensure the following conditions in order to successfully send the data.
- Common.EncodedMetadata AC feature is ON
- Content is base64 encoded
- Metadata size is limited to 5k
Failing to comply with the above validation points will cause the message to be dropped. This feature is only available for the messaging conversations not for chat conversations
Encoded Metadata can be sent with simple Text, Rich Content (structured content) and Multiple responses.
Sending Text Message with Encoded Metadata
For sending encodedMetadata with the response of your callback this property must be included in the context object. Be careful with the camel-case characters you must provide it exactly the same. An example of the simple two text message response is below:
encodedMetadata will be supplied to all the messages defined in messages property.
const payload = {
context: {
encodedMetadata: "ewoic29tZUluZm8iOiAiSSB3YXMgZW5jb2RlZCIKfQ==",
},
messages: [
"I am a text response with encoded metadata",
"I am another text response with encoded metadata",
],
};
Sending Rich Content (structured content) with Encoded Metadata
For sending encodedMetadata with the response of your callback this property must be included in the context object. Be careful with the camel-case characters you must provide it exactly the same. An example of the a simple text message and a rich content response is below:
encodedMetadata will be supplied to all the messages defined in messages property and also to rich content.
const payload = {
context: {
encodedMetadata: "ewoic29tZUluZm8iOiAiSSB3YXMgZW5jb2RlZCIKfQ==",
},
messages: [
"I am a text response with encoded metadata",
{
structuredContent: {
type: "vertical",
elements: [
{
type: "button",
click: {
actions: [
{
text: "Recommend me a movie, please",
type: "publishText",
},
],
},
title: "Recommend a movie",
},
],
},
},
],
};
If you want to apply encodedMetadata specific to a structured content then you can find below example where encodedMetadata with value ZGlmZmVyZW50IGVuY29kZWQgbWV0YWRhdGE= will be applied to the structured content message only. For the other messages encodedMetadata defined in the context will be applied.
const payload = {
messages: [
"Hi How are you doing?",
{
encodedMetadata: "ZGlmZmVyZW50IGVuY29kZWQgbWV0YWRhdGE=",
structuredContent: {
type: "vertical",
elements: [
{
type: "button",
click: {
actions: [
{
text: "Recommend me a movie, please",
type: "publishText",
},
],
},
title: "Recommend a movie",
},
],
},
metadata: {
type: "ExternalId",
id: "12345",
},
},
],
context: {
encodedMetadata: "ewoic29tZUluZm8iOiAiSSB3YXMgZW5jb2RlZCIKfQ==",
},
};
Sending Social Messages (Public Message) with Social Metadata
function lambda(input, callback) {
// Take a look at this guide to get further information about Social Messaging & Conversation Metadata
// https://developers.liveperson.com/messaging-agent-sdk-conversation-metadata-guide.html
const {
message,
convId,
context: { lpEvent: { metadata: umsMetadata = [] } = {} } = {},
} = input.payload;
const response = {
context: {
metadata: [],
},
messages: [],
};
const socialMetadata = umsMetadata.find(
(m) => m.type === "SocialMessagingEventData"
);
const addPrivateSMLinkMetadata = () => {
if (socialMetadata && socialMetadata.channel === "Public") {
const myMessage =
"I'm a BOT, please join to our private chat to talk with a live agent:\n https://m.me/" +
socialMetadata.conversationState.dmChatId;
// The following is an example of Facebook Public Replies
const socialMetadataResponse = {
type: "SocialMessagingEventData",
channel: "Public",
replyToId: `${socialMetadata.replyToId}`,
event: {
source: "Facebook",
type: "CC",
},
conversationState: {
currentChannel: "Public",
dmChatId: `${socialMetadata.conversationState.dmChatId}`,
},
};
// LEGACY
// See: Sending (single) Structured content via 'context' property (Legacy)
const structureContentSM = {
type: "vertical",
elements: [
{
type: "text",
text: myMessage,
alt: "sm-piggyback",
},
],
};
response.context.structuredContent = structureContentSM;
response.context.metadata.push(socialMetadataResponse);
// TRANSFER
// See: Transfer / Escalations
response.context.action = "TRANSFER";
response.context.actionParameters = { skill: "facebook" };
}
};
addPrivateSMLinkMetadata();
callback(null, response);
}
Sending Pause/Delay Message
It is possible to send an event of type "delay" before regular content events and actions. This specifies the time the bot will wait before displaying the next message. There are two properties, delay and typing, which need to be added in with the response body of the function.
- delay: The number of seconds which the bot will wait. These are expected to be only whole numbers for example for one second delay you will write 1 as a value
- typing: This property will enable/disable the typing indicator while delay is happening. It is optional; if not provided then the value will be considered as true
Setting a delay in between multiple messages is possible and an example of such a case (Message — Delay — Structured Content) can be seen below:
const payload = {
messages: [
"Hi I am a message before delay",
{
delay: 5,
typing: true,
},
{
structuredContent: {
type: "vertical",
elements: [
{
type: "button",
click: {
actions: [
{
text: "Recommend me a movie, please",
type: "publishText",
},
],
},
title: "Recommend a movie",
},
],
},
metadata: {
type: "ExternalId",
id: "12345",
},
},
],
};
Note: Using the delay as a single/sole response from the bot to the consumer is effectively a ‘no response’ action. This allows the bot to receive a consumer message without responding to the consumer.
Sending Private Text Message
It is possible to send a private text message from the Live Engage (LE-UI) via agent workspace. This feature can now be used via the Third-Party bots as well. This will allow Brands to define private message text within the conversational flow of the bot. These messages are published into the conversation for other Agent/Manger participants. This enables Brands to customize messages giving more insight, summarizing actions taken by the bot, or also advising on next actions the handover agent should take.
Please note If you have not migrated to new Agent Workspace you will not be able to see the Private message indicator in the conversation window. Nevertheless, private text messages will not be shown to the consumer and only remain visible to Agents and Managers.
Please note private text message will never be shown to the consumer and will be visible only inside the conversation window of agent workspace. There are two properties, text and messageAudience which need to be added in with the response body of the function.
| key | value | notes |
|---|---|---|
| text | any string value | mandatory |
| messageAudience | value should be "AGENTS_AND_MANAGERS" | case-sensitive, mandatory |
Setting a private text message between multiple messages (with action) is possible and an example of such a case (Simple Text Message — Private Text Message — Action) can be seen below:
const payload = {
messages: [
"Transferring",
{
text: "This is a private text",
messageAudience: "AGENTS_AND_MANAGERS",
},
],
context: {
action: "TRANSFER",
actionParameters: { skill: "human_skill" },
},
};
Invoke LivePerson Function
During a conversation, it is possible to trigger a different LivePerson Function. This provides a way to run additional custom logic with a bot.
To invoke a different LivePerson Function, we use the action key in the response object as we did for a transfer (see example above).
| key | value | notes |
|---|---|---|
| action | INVOCATION | case-sensitive, mandatory |
| lambdaUuid | lambda UUID of LivePerson Function | case-sensitive, mandatory |
| payload | content that will be sent to the LivePerson Function | case-sensitive |
| failOnError | boolean that decides if bot escalates on failed invocation | case-sensitive |
To retrieve the lambdaUuid of your LivePerson Function follow this guide
In addition, it is possible to send your own payload to the function. Set your content inside the payload parameter.
The bot does not escalate on a failed invocation by default. To enable this, set the additional parameter failOnError to true.
const payload = {
messages: [
"Please wait will I check if we have any live agents online that can attend to you",
],
context: {
action: "INVOCATION",
actionParameters: {
"lambdaUuid": "4ec49ffc-080b-4e59-b302-18d6b826191b",
"payload": "{ "some": "stuff"}",
"failOnError": true
},
},
};
Sending SIGNALED events (Messaging Only)
This Feature requires UMS 4.9
To send a signal to the channel not visible inside the normal conversation a bot can send the following event. Channels need to implement custom logic and listen on chat state events in order to react to it.
const response = {
messages: [],
context: {
action: "SIGNAL",
actionParameters: {
payload: {
testParam: 'testValue'
}
},
}
};
callback(null, response);
Engagement attributes as context
Third-Party bots allows the collection of engagement attributes (more information can be found here) if Engagement Attributes option is checked in the Conversation Type step as shown in Figure below.
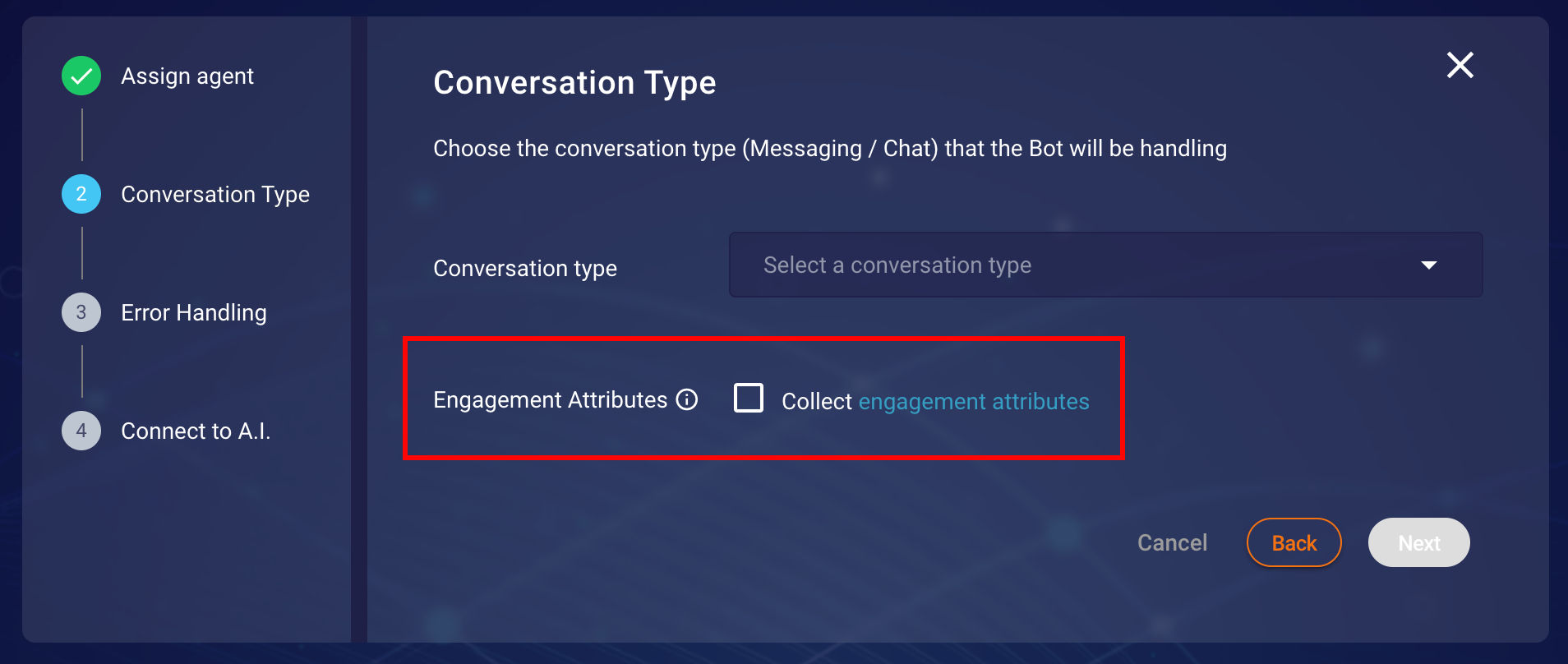 Figure showing Conversation Type step in creation/modification of bot configuration.
Figure showing Conversation Type step in creation/modification of bot configuration.
These attributes are only collected at the start of a conversation. Third-Party bots leverage the LivePerson Visit Information API to collect the engagement attributes, Further information Visit Information API can be found here. Moreover, Engagement attributes are not updated throughout the life cycle of a conversation and only passed along with each message request. In LivePerson functions Bot integration these engagement attributes are added to the property lpSdes. For the preservation of these attributes within a conversation context property is used. An example of the request body can be seen below:
const {
message,
convId,
event: { name: eventName = "" } = {},
context: {
lpEvent, // contains the original received raw connector event
lpSdes: { unauthenticatedSdes, authenticatedSdes }, // contains all collected lpSdes on conversation start if collecting is enabled
},
} = input.payload;
Receiving Rich Content Response (Messaging Only)
Third-Party Bots allows LivePerson's Rich Messaging channel capabilities not only to be received as a response from the vendor but also, allow Rich Messages (Structured Content) to be sent back to the vendor based on specific user interactions/responses (For example user sharing their location on WhatsApp). Please note these capabilities are sometimes limited by the channels in which the conversation is happening. For the list of Rich Messaging capabilities for each channel, browse or search the table here.
In LivePerson functions integration Rich Content Event (RichContentEvent) is passed via the property event which is part of another property lpEvent
that is sent with context information. An example of the request body containing RichContentEvent can be seen below:
const {
message,
convId,
context: {
lpEvent: {
event: { type, content }, // this contain the RichContentEvent
},
},
} = input.payload;
A sample RichContentEvent request of a user who shared location via WhatsApp will look like this:
{
"convId": "abcdefg-1234-a1b2-6787-fkljwuhs7yk2",
"context": {
"lpEvent": {
"event": {
"type": "RichContentEvent",
"content": {
"type": "vertical",
"elements": [
{
"type": "map",
"la": 49.82380908513249,
"lo": 2.021484375,
"alt": "49.82380908513249, 2.021484375"
}
]
}
},
"lpSdes": {}
},
"message": "com.liveperson.bot-connectors.consumer.send-rich-content" // Message from Third-Party Bots will be sent as this value
}
A minimal LivePerson function code for the demonstration of WhatsApp sharing location can be seen below. This LivePerson function will
check if the input payload has RichContentEvent then will respond with the entire body.
function lambda(input, callback) {
const payload = {
messages: [],
context: {},
};
const {
message,
context: { lpEvent: { event: { type = "", content = {} } = {} } = {} } = {},
} = input.payload;
if (message && message.toLowerCase() === "hi") {
payload.messages.push("Hi there! How can I help you today?");
} else if (
message &&
message === "com.liveperson.bot-connectors.consumer.send-rich-content" &&
type === "RichContentEvent"
) {
payload.messages.push(
`I received a rich content it contains: ${JSON.stringify(input.content)} `
);
} else {
payload.messages.push("I am sorry I don't understand. Can you repeat?");
}
callback(null, payload);
}
We can see the above LivePerson function in action below:

Receiving Last consumer message (Messaging Only)
When an ongoing conversation gets transferred to a bot connected via the Third-Party Bot connector, the connector forwards the last consumer message to the AI vendor as part of the the welcome event. This allows the bot to react to the last consumer message instead of instantiating a new conversation.
In the LivePerson Functions integration, the last consumer message is passed via the property lastConsumerMessage that is sent with context information as part of lpEvent data. An example of the request body containing WelcomeEvent can be seen below:
const {
message,
convId,
context: {
lpEvent: {
type,
content,
lastConsumerMessage
} // this contain the ContentEvent with content value `welcome`
}
} = input.payload;
A minimal LivePerson function code for the demonstration can be seen below. This LivePerson function will
check if the input payload has ContentEvent with the value welcome and the lastConsumerMessage not empty then will respond with the entire body.
function lambda(input, callback) {
const payload = {
messages: [],
context: {},
};
const {
message,
context: {
lpEvent: {
lastConsumerMessage = "",
type = "",
content = ""
} = {}
} = {},
} = input.payload;
if (message && message.toLowerCase() === "hi") {
payload.messages.push("Hi there! How can I help you today?");
} else if (
lastConsumerMessage &&
content === "welcome"
) {
payload.messages.push(
`the last consumer message is: ${lastConsumerMessage} `
);
} else {
payload.messages.push("I am sorry i don't understand. Can you repeat?");
}
callback(null, payload);
}
Receiving signaled events (Messaging Only)
This Feature requires UMS 4.9
If SIGNALED events are enabled in the Conversation Type settings the bot will be able to receive this kind of chat state events.
const {
convId,
event: {
name, // === 'SIGNAL'
data: {
payload // the metadata payload string
}
}
} = input.payload;
Send Secure Forms (PCI)
Secure forms are configured by LivePerson. To enable this feature, please contact LivePerson customer support or your account team. Your LivePerson account team will work with you make the necessary adjustments to your account settings and configurations. For additional information regarding secure forms: Community Center
To give agents the permission to read secure forms sent by a bot, please contact LivePerson customer support to enable the site setting: messaging.display.secure.form.sent.by.bots
Bots are able to send a secure form to a conversation and transfer the customer after submission. The transferred conversation is then visible by an eligible agent, that can read and process the submitted form data.
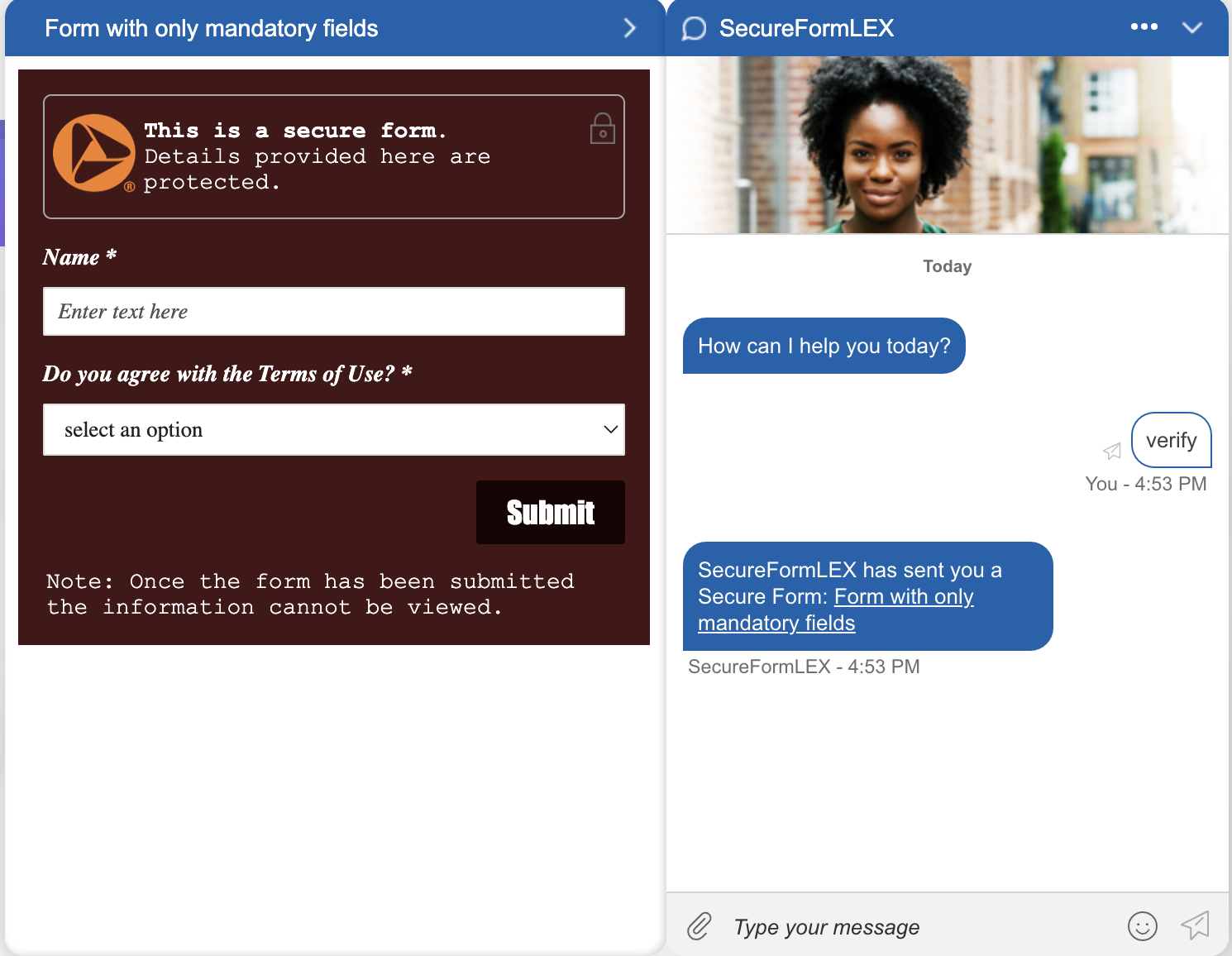
To enable this feature in LivePerson Functions, you need to Action response in the Function. The response needs to send a SEND_SECURE_FORM action including the unique formId of the form, that should be provided from LivePerson after the creation of one secure form, and the title of the form.
To transfer the conversation after submission to an eligible user that can process the secure forms, you need to create a new intent listening on the utterance FORM-SUBMISSION-INTENT that transfers the conversation using a basic transfer event.
A minimal working function is shown below:
function lambda(input, callback) {
const {
message,
convId,
event: {
name: eventName = ""
} = {}
} = input.payload;
const response = {
context: {},
messages: []
}
const AccountIdentificationIntents = ['Verification', 'Verify', 'Identify', 'Account Identify', 'Account Identification', 'Account Verification'];
// If one of the intents matches the message, send a secure form
if (message && AccountIdentificationIntents.some(intent => message.toLowerCase().includes(intent.toLowerCase()))) {
response.context = {
action: "SEND_SECURE_FORM",
actionParameters: {
formId: 4510014332,
title: "Form with only mandatory fields"
}
};
}
// Transfer the conversation after form submission
else if (eventName === "FORM_SUBMISSION") {
response.messages.push("Form submitted. I will transfer you now.")
response.context = {
action: "TRANSFER",
actionParameters: {
skill: "secure",
},
}
}
// Basic echo function implementation
const responseMessage = (eventName === "welcome") ? "Welcome! I'm responding as fast as LivePerson Functions." : message;
if (Object.keys(response.context).length === 0 && response.messages.length === 0) {
response.messages.push(responseMessage);
}
callback(null, response);
}