Automatic Messages (also known as System Messages or Auto Messages) are predefined messages triggered upon events that occur through the lifecycle of a conversation (e.g. the consumer opens a new conversation, the conversation is transferred to another agent time to respond is updated). Automatic Messages will be sent to both agent and consumer by the system. Therefore they appear in the conversation's history both on the consumer and Conversational Cloud side.
Thanks to our integration with Automatic Messages, you can create functions triggered based on selected events. A payload is sent to a function containing metadata related to the specific conversation and based on the selected event during the invocation. This payload can then be used for further processing and referencing.
A function might trigger regardless of the state of the enabled flag of an Automatic Message. To avoid a function being triggered, you must undeploy your function. You can choose to ignore a specific event by leveraging the cbotEventType property included in the invocation payload. However, the ignored invocations here would still count towards your usage limits.
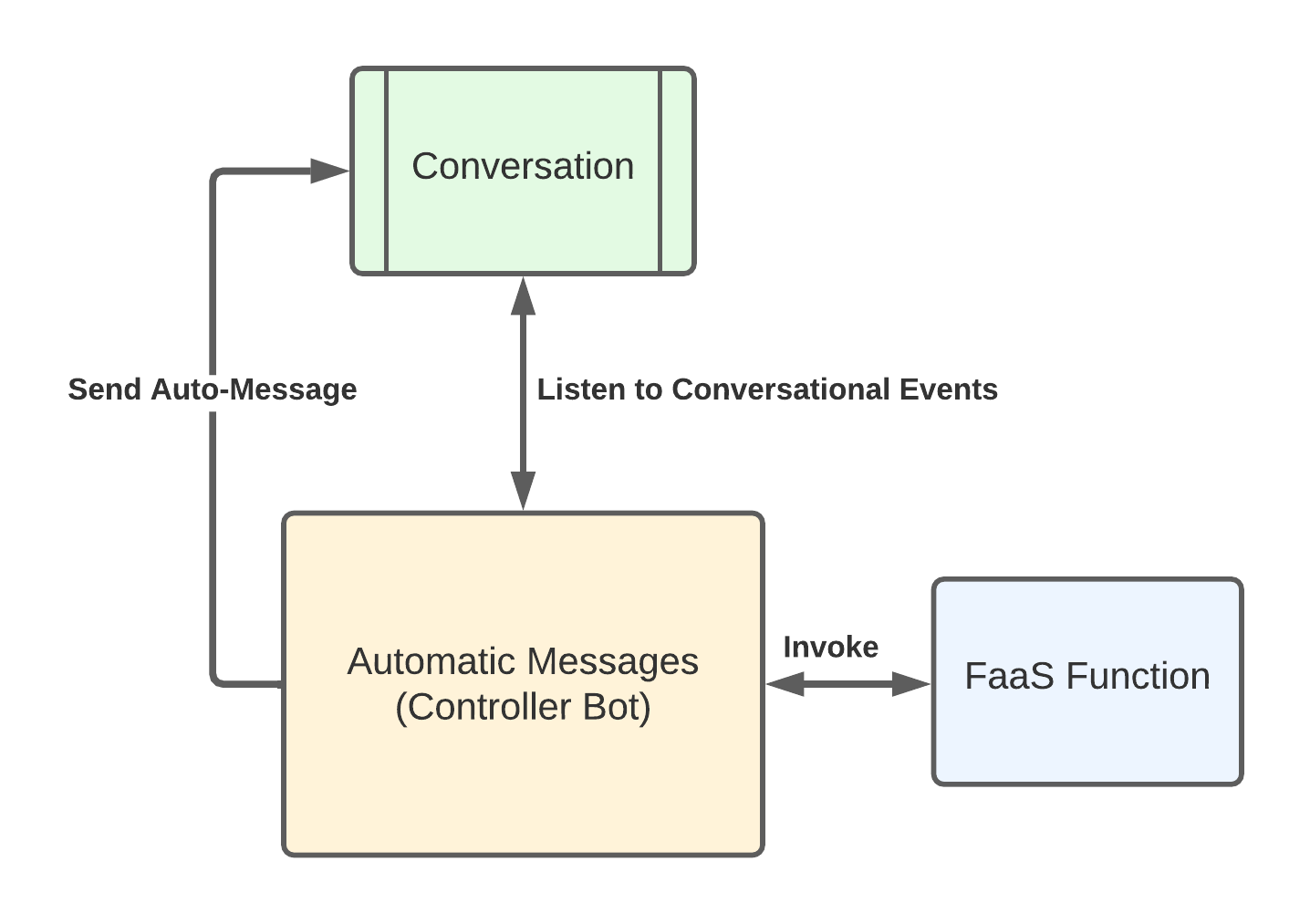
This is the Automatic Messages flow with Functions integration:
- Automatic Messages listens to conversation events.
- If there is an Auto-message configured for the event, it will send that message to the conversation.
- If there is a Function deployed associated with that event, the function will be invoked.
- After invocation, automatic Messages will check the response and will perform one of the following actions based on the callback payload:
- Transfer Conversation to a different Skill.
- Transfer Conversation to a different Agent.
- Send a message.
- Close the Conversation.
- Do nothing.
Configuration
Step 1 — Enable Automatic Messages
Enable the Automatic Messages feature.
Your account must have the Automatic Messages permissions enabled; please get in touch with your account team to enable the feature.
Step 2 — Create a function
Create a new function using one of the following messaging events:
- Messaging new conversation.
- Messaging conversation end.
- Messaging conversation routing.
- Messaging participants change.
- Messaging TTR.
- Messaging Line in Off-Hours
- Messaging consumer step up.
- Messaging conversation idle.
- Messaging conversation consumer idle.
- Messaging conversation agent idle.
- Messaging conversation stuck queue idle.
You can select one of the available templates for the chosen event. Currently, you can create only one function per template type for these conversational events. If multiple implementations of an event are necessary, you can achieve this with anOrchestrator Function. Leveraging this feature, you can invoke multiple functions from the same (orchestrator) function.
You can select a Skill or set of Skills. Specifying a Skill can reduce the complexity of the function's code, reducing the number of unnecessary invocations.
Step 3 — Edit your Function
Adjust the code of the template according to your needs. The function can return a series of commands to the trigger. Please see our Deep Dive UI Creation Process section or alternatively Deep Dive CLI Create section for further information.
Step 4 — Deploy your function
Like any other function, this function must be deployed before it can be used. Please see our Deep Dive UI Deployment Process section or alternatively Deep Dive CLI Deploy section for more information on how to deploy your function. At this point, you can also test your function.
Messaging events
Conversational Cloud Messaging uses a series of "Conversation State Change Events", fired when specific actions or events occur within the conversation. You can use these events to trigger your functions. The Automatic Messages are responsible for invoking functions on certain messaging events.
Multiple conversation event types are mapped to the same invocation messaging event.
A deployed function on a specific messaging event can be invoked on multiple conversation events. For example, a function deployed on the Messaging conversation end event will fire when one of these events occurs during a conversation: AGENT_END_CONVERSATION, CONSUMER_END_CONVERSATION and SYSTEM_END_CONVERSATION.
The cbotEventType property is included in the invocation payload to distinguish the conversation event type during the invocation. The following table shows the conversation event type mapping to messaging events on functions:
| Event Type | Mapped to |
|---|---|
| CONSUMER_OPEN_NEW_CONVERSATION_FIRST_TIME_OFF_HOURS | Messaging new conversation |
| CONSUMER_OPEN_NEW_CONVERSATION_OFF_HOURS | Messaging new conversation |
| CONSUMER_OPEN_NEW_CONVERSATION_FIRST_TIME | Messaging new conversation |
| CONSUMER_OPEN_NEW_CONVERSATION | Messaging new conversation |
| CONSUMER_OPEN_NEW_CONVERSATION_AFTER_AUTOCLOSE | Messaging new conversation |
| AGENT_END_CONVERSATION | Messaging conversation end |
| CONSUMER_END_CONVERSATION | Messaging conversation end |
| SYSTEM_END_CONVERSATION | Messaging conversation end |
| ENGAGEMENT_TRANSFERED | Messaging conversation routing |
| YOU_ARE_CONNECTED_TO | Messaging participants change |
| BACK_TO_QUEUE | Messaging participants change |
| JOINED_AGENT_LEFT_CONVERSATION | Messaging participants change |
| ANOTHER_AGENT_JOINED_CONVERSATION | Messaging participants change |
| AGENT_UPDATED_RESPONSE_TIME | Messaging TTR |
| CONSUMER_CANCELED_URGENT_RESPONSE_TIME | Messaging TTR |
| CONSUMER_ASKED_URGENT_RESPONSE_TIME | Messaging TTR |
| CONSUMER_SEND_MESSAGE_ON_OFFHOURS | Messaging Line in Off-Hours |
| CONV_AWAITING_IN_QUEUE | Messaging conversation idle, Messaging conversation stuck idle |
| AGENT_NON_RESPONSIVE | Messaging conversation idle, Messaging agent idle |
| CONSUMER_NON_RESPONSIVE | Messaging conversation idle, Messaging consumer idle |
| CONSUMER_STEP_UP | Messaging consumer step up |
If there is a function with Messaging conversation idle event, you cannot create other function with any of the events Messaging conversation stuck idle, Messaging agent idle or Messaging consumer idle and vice versa.
Interaction via Commands
You can send commands back to the trigger by returning one command or multiple commands by simply adding them to an array. Using callback commands is not mandatory. If you do not want to take any actions, return an empty array []. This will result in no operation.
If no message is set in the result of the function (which it returns to the trigger, for example: callback(); ), the default automatic message for the account will be triggered.
Please be aware of race conditions that can be introduced related to the issued commands. E.g. Adding both Message & Close command can yield to a situation where the conversation is closed without the message being send. Further if you add two commands of the same type e.g. two transfer commands only the the first command will be processed.
let result = [
{
type: "systemMessage", // Returns a system message into the conversation
text: "your message"
},
{
type: "transfer", // Transfers the conversation.
skillId: "123456", // Transfer to different Skill.
agentId: "123456" // Propose an agent.
}
]
callback(null, result);
With Automatic Messages selected as trigger, you have the option to execute the following commands:
- Send a message. The default automatic message can be overwritten with:
let result = [
{
type: "systemMessage", // Returns a system message into the conversation
text: "your message",
}
]
callback(null, result);
- Transfer Conversation to a different Skill:
let result = [
{
type: "transfer", // Transfers the conversation.
skillId: "123456", // Transfer to different skill.
}
]
callback(null, result);
- Transfer Conversation to a different Agent (to configure this feature see here):
let result = [
{
type: "transfer", // Transfers the conversation.
agentId: "123456", // Transfer to different skill.
}
]
callback(null, result);
- Close the Conversation:
let result = [
{
type: "closeConversation" // Closes the conversation
}
]
callback(null, result);
Please be aware that if you close a conversation using closeConversation it will not trigger the Messaging Conversation End event.
Best Practices
Messaging events are asynchronous
Functions for messaging listens for messaging events asynchronously. Consequently, this can cause race conditions with other parts of the Conversational Cloud. Therefore, it is considered best practice to use bots instead of Functions for implementing routing logic. Routing via Functions makes sense whenever a conversation is in a stagnant state (i.e. not in the process of being routed), e.g. a conversation is idle, or a message line has been sent in off-hours. Functions are an excellent option to enrich data with third-party systems like CRMs or save data in the Conversation Context Service to make it usable by another system like this, the Conversation Orchestrator.
If the authenticated consumer's previous conversation was auto-closed and the new one opened within 48 hours, the new conversation event will not be triggered.
Automatic Messages Error Handling
If your function invocation takes too long or you have errors in your code, Automatic Messages will retry up to 3 times. This will increase the number of invocations when your function does not perform well and lead to more overload.
Payload Details
| 1. level | 2. level | 3. level | description | type | example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| end | closeReason | which role closed conversation | STRING | AGENT/CONSUMER/SYSTEM | |
| general | cbotEventType | Original conversation event type | STRING | CONSUMER_OPEN_NEW_CONVERSATION_FIRST_TIME_OFF_HOURS | |
| general | type | notification type | STRING | UPSERT | |
| general | convId | ID of conversation | STRING | c840e51e-5f65-4ad4-8d34-5c82b99a2200 | |
| general | dialogId | ID of dialog | STRING | c840e51e-5f65-4ad4-8d34-5c82b99a2200 | |
| general | sessionId | ID of session | NUMBER | 1528463744580 | |
| general | startTs | conversation start time as timestamp | NUMBER | 1528463744663 | |
| general | effectiveTTR | timestamp when agent should be available | NUMBER | 1528464044687 | |
| general | oldConvState | previous state of the dialog | STRING | CLOSE | |
| general | newConvState | current state of the dialog | STRING | OPEN | |
| general | contexttype | type of cotext | STRING | SharkContext | |
| general | campaignInfo | id | ID of campaign | NUMBER | 2327699812 |
| general | campaignInfo | engangementId | ID of engangement | NUMBER | 2327699912 |
| general | clientLanguage | language of the client device | STRING | en-US | |
| general | clientFeatures | list of supported client features | ARRAY | ["AUTO_MESSAGES", "MULTI_DIALOG"] | |
| general | inOffHours | shift-status of the contact center | BOOLEAN | TRUE/FALSE | |
| general | visitorId | ID of visitor | NUMBER | 1528463744580 | |
| general | originatorId | ID of originator | NUMBER | 37607275.23 | |
| general | originatorPid | Pid of originator | STRING | f39fbc5f-da77-5417-8bc7-7584efdd1a5e | |
| general | originatorMetadata | id | Pid of originator of metadata change | STRING | f39fbc5f-da77-5417-8bc7-7584efdd1a5e |
| general | originatorMetadata | role | Role of originator of metadata change | STRING | CONTROLLER |
| general | serverTimestamp | timestamp of the server | NUMBER | 1528463781807 | |
| general | clientIpAdress | IP Address of client | STRING | 172.26.138.38 | |
| general | manualETTR | time to response manually updated by agent | STRING | 1541152938069 | |
| general | lastMessageComposer | the role of the last composer | STRING | CONSUMER | |
| general | lastMessageTs | timestamp of last message | NUMBER | 1541152938069 | |
| general | lastAgentMsgTs | timestamp of last agent message | NUMBER | 1541152938069 | |
| general | backToQueueTs | timestamp when the conversation was returned to queue | NUMBER | 1541152938069 | |
| idle | lastConsumerMsgTs | timestamp of last consumer message | NUMBER | 1541152938069 | |
| idle | agentNonResponsive | time | time that should pass after consumer's last message in order the agent to be non-responsive | NUMBER | 30 |
| idle | agentNonResponsive | timeUnits | time units in which agent non-responsive time should be calculated | STRING | minutes |
| idle | consumserNonResponsive | time | time that should pass after agent's last message in order the consumer to be non-responsive | NUMBER | 30 |
| idle | consumserNonResponsive | timeUnits | time units in which consumer non-responsive time should be calculated | STRING | minutes |
| idle | convNotTakenTime | time | time units in which conversation idle time should be calculated | STRING | minutes |
| idle | convNotTakenTime | timeUnits | how long should the conversation stay in queue in order to be idle | NUMBER | 30 |
| mid | openedInOffHours | indicator if the conversation was opened in off hours | BOOLEAN | TRUE/FALSE | |
| participantChange | oldParticipants | array of the participants of the previous state | ARRAY | [{"id": "f9d58c57-c489-45f5-bae4-c5ebd52b3972","role": "ASSIGNED_AGENT"}] | |
| participantChange | newParticipants | array of the participants of the current state | ARRAY | [{"id": "f9d58c57-c489-45f5-bae4-c5ebd52b3972","role": "ASSIGNED_AGENT"}, {"id": "f9d58c57-c489-45f5-bae4-c5ebd52b3972","role": "AGENT"}] | |
| routing | oldSkillId | previous skillId of conversation | STRING | 563268 | |
| routing | newSkillId | current skillId of conversation | STRING | 563267 | |
| start | firstConversation | if this is the frist conversation of the consumer ever | BOOLEAN | TRUE/ FALSE | |
| ttr | oldTtr | ttrType | type of ttr of the previous state | STRING | NORMAL |
| ttr | oldTtr | value | value of ttr of the previous state | NUMBER | 600 |
| ttr | newTtr | ttrType | type of ttr of the new state | STRING | URGENT |
| ttr | newTtr | value | value of ttr of the new state (after change for example to URGENT) | NUMBER | 300 |