You may integrate the Web Tag for a single LivePerson account across two or more websites with different base domains (for example, a.com and b.com) or different sub-domains (for example, a.example.com and b.example.com). Web messaging is supported in this use case, and there is also capability to maintain the consumer's experience "across domains", also known as cross-domain.
This page explains LivePerson’s web messaging support for persisting the consumer’s identity, conversation, and other information while they navigate across different domains.
Example use case:
- Consumer starts a conversation on a webpage on
a.comthat is tagged with your LivePerson account's Web Tag. - Consumer navigates to a webpage on
b.comthat is also tagged with your LivePerson account's Web Tag. - The same conversation automatically loads on the
b.comwebpage (expected "cross-domain" behavior).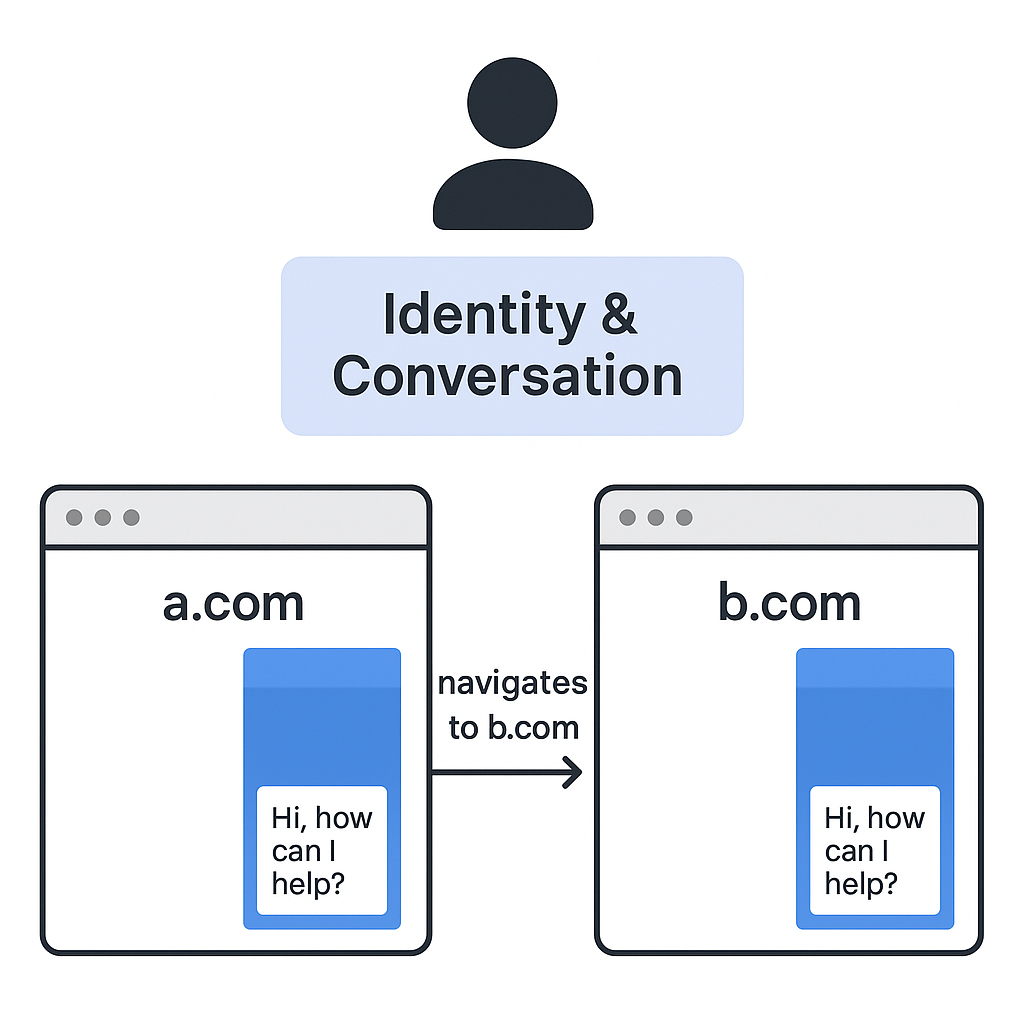
Unauthenticated cross-domain web messaging
The “Cross-Domain” feature
This account feature (when activated) enables a web messaging consumer's unauthenticated identity, conversation, and other information to persist while navigating between multiple sites that possess different base domains or different sub-domains, provided that all sites are tagged with the same LivePerson account.
This enables a seamless, continuous experience for consumers across sites that the LivePerson account declares/configures as "Monitored Domains".
If the LivePerson account has the Cross-Domain feature enabled, the different domains configured in “Monitored Domains”, and the current web messaging consumer is using a capable supported browser, then the consumer’s unauthenticated identity, conversation, and other information will be persisted across domains.
Browser support
Due to modern browser limitations and privacy initiatives support is limited to only certain browsers/OSes…
Where the unauthenticated Cross-domain feature is supported:
- Chrome on Windows, macOS, and Android with default privacy settings ✅
- Edge on Windows and macOS with default privacy settings ✅
Where the unauthenticated Cross-domain feature is NOT supported:
- Not on Firefox or Safari on any operating system ❌
- Not on any browsers on iOS (Safari, Chrome, Edge, Firefox), as Apple forces all browsers there to use Apple’s WebKit, which inherits the behavior from Safari ❌
- Not on Edge on Android due to stricter default privacy settings on Android versus on other operating systems. ❌
- Not in "incognito mode" or any private browsing modes in any browser and operating system ❌
- Not with 3rd-party cookies/storage disabled in settings in any browser and operating system ❌
Read more about browser limitations here: Browser Storage Partitioning
Expected support matrix (with default browser privacy settings):
| Windows | macOS | Android | iOS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chrome | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Edge | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Firefox | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Safari | n/a | ❌ | n/a | ❌ |
As the browser support above represents approximately 70% of global browser market share, it functionally means that this behavior will be consistent across the majority of web users. Sources: 1 / 2 / 3
Other notes and limitations
- All browser support sited above is considered "best-effort" and depends on a number of factors at runtime, including browser limitations, browser settings, extensions, Ad-blockers, etc.
- The Cross-Domain feature can only be enabled or disabled for new conversations; it will not affect any active discussions.
- This feature officially supports Web "Messaging" engagements and does not extend to legacy "Chat" engagements.
- If a consumer attempts to navigate to a tagged website that is not included in the Monitored Domains whitelist (due to misconfiguration or potential fraud) while an engagement window is open, they will encounter the following error: "Cannot resume conversation, please return to the previous page to continue." As a result, no engagement will be available on that domain.
- CoBrowse is designed to function smoothly within the domain where the chat was initiated. However, if the user switches to a different domain, the conversation will persist without the CoBrowse session.
How to configure for an account
Follow the instructions on this Knowledge Center page to configure unauthenticated cross-domain web messaging for your account.
How does it technically work?
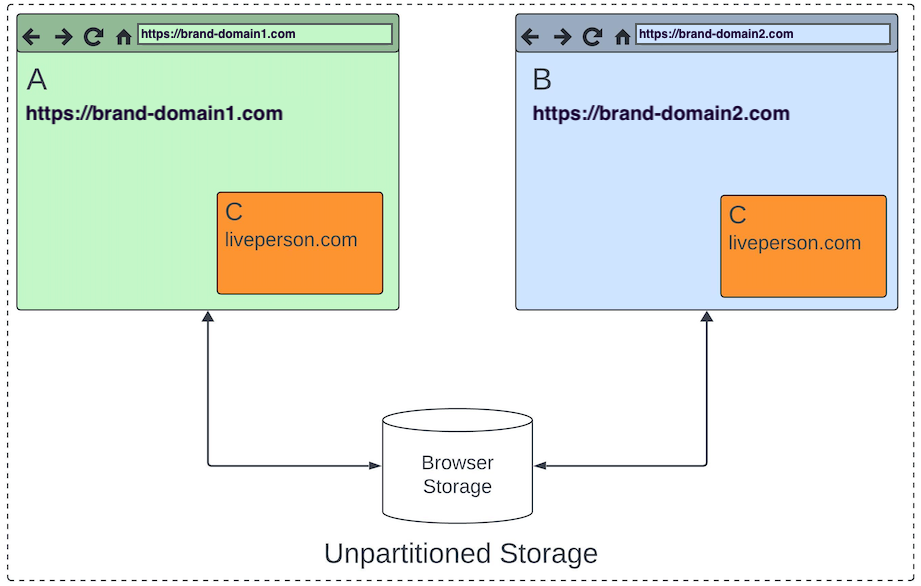
This technically works by utilizing 3rd-party, non-cookie browser storage set to one of LivePerson's domains, which historically browsers made available to each of the account's configured "monitored" sites across different domains.
LivePerson's domain ("C" - lpsnmedia.net) can store data when embedded in one top-level site ("A" - brand-domain1.com), and then access that same data when embedded in another top-level site ("B" - brand-domain2.com).
In other words, LivePerson's storage context is shared between the different/unique list of "monitored" sites it is embedded in.
Secure Storage
This is accomplished using the Secure Storage component LivePerson has implemented. It is a client-side storage component that encapsulates browser storage actions (set, get, remove actions) by selecting the best available native storage based on browser capability (indexedDB, localstorage, cookies / secure session cookie, or sessionStorage, in that order).
Secure Storage handles data expiration, tests to select the best storage possible, and restricts data access only across configured managed domains.
The ability to access this data across domains is primarily enabled by the browser Storage Access API under the hood.
Essential data
For an unauthenticated web messaging identity and conversation to persist, the following data in browser storage is a bare minimum:
| Data | Description | Why is it needed? |
|---|---|---|
Shark visitor IDLPVID
|
Monitoring consumer identifier | - Identifies the consumer to the monitoring service (Shark) |
Shark session IDLPSID-{accountID}
|
Monitoring session identifier | - Identifies the session to the monitoring service (Shark) |
| Unauthenticated consumer JWT | Anonymous/unauth consumer token | - Used to grant access to a conversation via the messaging engine (UMS) |
| Unauthenticated consumer ‘sub’ | Anonymous/unauth consumer identifier (contained in the JWT) | - Also identifies the consumer to the monitoring service (Shark) - Shark needs this to return an “open conversation” state - Can likely be derived from jwt, but would be better if we didn’t need the jwt (see Optimizations below) |
Authenticated cross-domain web messaging
LivePerson web messaging supports authenticated consumer identities in addition to unauthenticated.
While unauthenticated identities are generated anonymously by LivePerson and stored in browser storage, authenticated identities are provided by your website on each page.
This means that authenticated cross-domain web messaging doesn't require a specific feature to be enabled, and doesn't have the same limitations as unauthenticated messaging does with browser storage.
The "Cross-Domain" feature (optional)
Enabling the Cross-Domain feature is not required for authenticated identities and conversations to persist across different domains, as in that case the consumer's authenticated identity is provided by you on each page, and not completely dependent on browser storage like unauthenticated identities are.
In some cases you still might choose to enable Cross-Domain with authenticated engagements in order to support "Step-Up" flows (unauthenticated "step up" to authenticated), and/or persist other non-identity information across domains.
Browser Support
Since the consumer's identity is provided by your website on each page, and not persisted in browser storage, cross-domain functionality to persist the authenticated identity should work in all supported browsers for LivePerson web messaging (recent versions of Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Safari).
This depends on the your ability to properly implement authenticated messaging, including authenticating the user on your side, and passing the authenticated identity to LivePerson as documented.
To persist other non-identity information, the Cross-Domain feature will still be needed.